How Do You Know if Your Dog Is in the Last Stages of Cushings Deseas2
What is Cushing'due south illness? 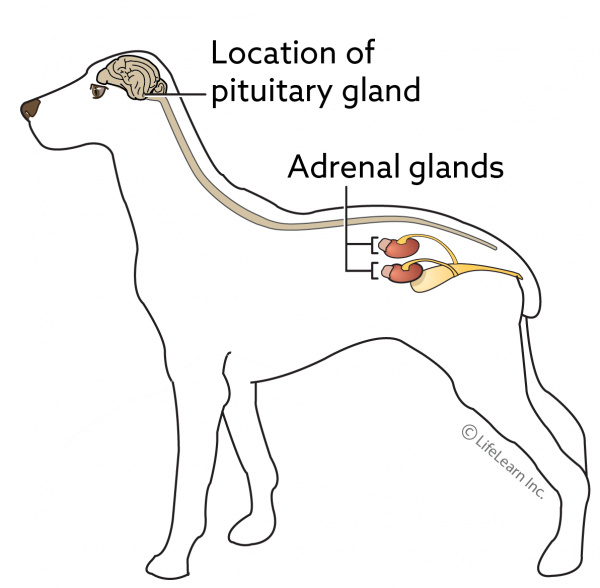
Cushing's disease (too known equally Cushing'south syndrome) is a status in which the adrenal glands overproduce sure hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. Literally translated, "hyper" means over-active, "adreno" means adrenal gland, and "corticism" refers to the outer part (cortex) of the adrenal gland.
The adrenal glands are located near the kidneys and produce several vital substances that regulate a variety of trunk functions and are necessary to sustain life. The almost widely known of these substances is cortisol, commonly known every bit cortisone. Decreased or excessive production of these substances, specially cortisol, may be life-threatening.
What causes this affliction?
There are 3 types of Cushing's disease, each of which has a unlike cause. Identifying the crusade is important considering each blazon is treated differently, and each has a different prognosis (expected outcome).
"Identifying the cause of Cushing's affliction is important because each blazon is treated differently and each has a different prognosis."
Pituitary gland tumor. The nigh common cause of Cushing'southward affliction (85% - 90% of all cases) is a tumor of the pituitary gland (which is located at the base of the brain). The tumor may be either beneficial (harmless) or malignant (cancerous). The tumor causes the pituitary gland to overproduce a hormone (ACTH) that stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. As shown in the illustration below, as the pituitary gland produces more ACTH, information technology triggers the adrenal glands to produce more cortisol. If the pituitary senses increased levels of cortisol, information technology will produce less ACTH, thereby reducing production of cortisol.
Pituitary gland tumors may be microscopic or large. Depending on the size of the tumor, clinical signs other than those of Cushing'due south disease may exist present, since a large tumor might press on or interfere with nearby structures in the area. More often than not, if the activeness of the adrenal gland can exist controlled, many dogs with this form of Cushing'south disease tin alive normal lives for many years, as long as they take their medication and stay under close medical supervision. If the pituitary tumor grows, it will affect the brain, often r 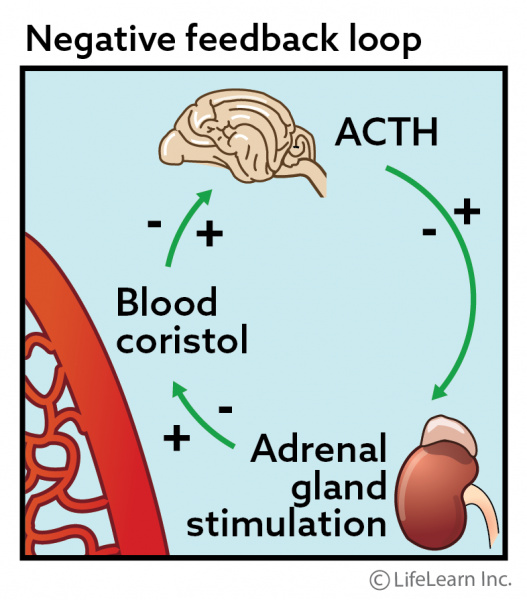
Adrenal gland tumor. Cushing'southward disease may be the consequence of a benign or malignant tumor of the adrenal gland itself (adenoma or carcinoma, respectively). If the tumor is benign, surgical removal will cure the affliction. If the tumor is malignant, surgery may help for some time, but the prognosis is much less favorable.
Excessive cortisol from prolonged apply of steroids. The third type of the illness is called iatrogenic Cushing'south affliction. It is acquired when there is excessive administration of an oral or injectable steroid. Although the steroids were usually given for a legitimate medical reason, in this case, their excess has go harmful to the patient.
What are the clinical signs of Cushing's illness?
Regardless of the type, the clinical signs of Cushing's disease are essentially the same. The most common clinical signs are an increase in ambition, increment water consumption, and urinating more. The increased ambition is a direct result of elevated levels of cortisol, which stimulate ambition. Lethargy (drowsiness or lack of activeness) and a poor hair glaze are as well common in pets with hyperadrenocorticism.
"Many dogs with Cushing's disease develop a bloated or pot-bellied appearance."
Many of these dogs develop a bloated or "pot-bellied" appearance to their abdomen because of an increase of fat inside the abdominal organs and a stretching of the abdominal wall equally the organs get heavier. The pot-bellied advent as well develops because the muscles of the intestinal wall go weaker and eventually atrophy (compress in size). Panting, sparse skin, chronic peel infections (pyoderma), dark-colored spots (hyperpigmentation), skin mineralization (calcinosis cutis), poor skin healing, and persistent bladder infections are other mutual clinical signs with this disease.
How is Cushing's disease diagnosed?
A number of tests are used to diagnose and confirm Cushing'southward affliction. The two most common tests to detect Cushing's illness are the ACTH stimulation test and the low-dose dexamethasone suppression (LDDS) test.
Endogenous ACTH levels (the level of the hormone ACTH in the body), a high-dose dexamethasone suppression (HDDS) examination, or a urine cortisol:creatinine ratio, are other tests that may be used to assist determine the type of the affliction.
"An abdominal ultrasound can exist a valuable part of the diagnostic process for Cushing's disease."
An abdominal ultrasound exam can be a valuable part of the diagnostic process for Cushing's disease. Ultrasound lets your veterinarian encounter the adrenal glands and determine their size and the presence of a tumor.
Although some of these tests can exist expensive, they are necessary to determine the all-time treatment and prognosis for your pet. Come across handout "Cushing'due south Disease - Testing" for further information on testing for Cushing'due south disease.
What are the treatment options?
Equally previously mentioned, the treatment depends on which type of the disease is present.
Pituitary tumor. Treatment of the pituitary-induced form of Cushing'due south illness is the most complicated. Two drugs, trilostane (brand name Vetoryl®) and mitotane (brand name Lysodren®), are commonly used. Selegiline hydrochloride (brand proper noun Anipryl®), and ketoconazole (brand name Nizoral®) are also used to treat canine Cushing'southward illness, although they are not considered as effective as trilostane or mitotane.
Adrenal tumor. Treatment of an adrenal tumor requires major intestinal surgery. If the surgery is successful (the unabridged tumor is removed) and the tumor is not malignant, there is a skilful hazard that the domestic dog will regain normal health. If surgery is non an option, some of these patients can be managed with medication, as discussed below.
Iatrogenic Cushing'south affliction. Handling of this class requires discontinuation of the steroid being given. This must exist washed in a controlled, gradual manner and so that other complications practice not occur. Unfortunately, information technology usually results in a recurrence of the disease that was beingness treated by the steroid. Because the steroid may have acquired adverse effects on the adrenal glands, treatment is also often needed to assist supplant the hormones that the adrenal gland ordinarily produces.
What practise I need to know if my dog's disease is being managed with medication?
Your veterinarian will outline a treatment program for your pet's specific condition. Be sure to follow his or her guidelines closely, considering these treatments frequently depend on consistent and regular administration of the medication. Lifelong treatment may exist necessary.
"Most dogs can be successfully treated with few medication side-furnishings."
Near dogs can be successfully treated with few medication side-effects. However, your pet must be carefully monitored using blood tests and clinical signs. Follow-up blood tests are very important to be certain your pet is receiving the proper dosage and not likewise fiddling or too much of the drug, both of which can cause complications.
What is the prognosis?
Although neither medical handling can cure a dog with Cushing's disease, command is possible for many years if the tumor is small. If the tumor is large and affects the brain, the pet has a less favorable prognosis. The prognosis for patients diagnosed with malignant adrenal tumors is guarded to poor. In cases of benign adrenal tumors, however, surgery is usually curative.
Source: https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/cushings-disease-in-dogs
0 Response to "How Do You Know if Your Dog Is in the Last Stages of Cushings Deseas2"
Postar um comentário